
Diabetes
Diabetes
Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a chronic metabolic disorder caused by the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. Insulin is a vital hormone secreted by the pancreas, responsible for helping the body use glucose (sugar) from food to generate energy. When insulin function is impaired, glucose accumulates in the blood, leading to serious health complications.
Causes of Diabetes
Several factors contribute to the development of diabetes, including:
- Genetics: Diabetes can run in families, especially if close relatives have the condition.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy eating habits, sedentary lifestyles, obesity, and being overweight significantly increase the risk.
- Stress and Mental Strain: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and disrupt metabolic functions.
- Metabolic Disorders: Some individuals develop diabetes due to glucose metabolism dysfunctions in the body.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Symptoms vary based on the type and stage of diabetes. Common signs include:
- Frequent thirst and urination: Excessive thirst and frequent urination are key indicators of diabetes.
- Fatigue: The body cannot efficiently use glucose, leading to persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Unexplained weight loss: Despite normal or increased appetite, some individuals lose weight unexpectedly.
- Frequent infections: Weakened immunity makes individuals more prone to urinary tract and skin infections.
- Slow-healing wounds: Poor blood circulation and nerve damage slow down the healing process.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is classified into three main types:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
- An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Commonly diagnosed in children and young adults.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
- The most prevalent form, occurring when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively.
- Strongly linked to lifestyle factors, including poor diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity.
- Typically develops in adults, but cases among younger individuals are rising.
3. Gestational Diabetes
- Develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
- Increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Complications of Diabetes
If not properly managed, diabetes can lead to severe complications, including:
- Cardiovascular diseases – Increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and hypertension.
- Kidney damage – Chronic kidney disease due to damage to small blood vessels in the kidneys.
- Vision impairment – Diabetic retinopathy, which can lead to blindness.
- Nerve damage (Neuropathy) – Causes tingling, pain, and loss of sensation, particularly in hands and feet.
Diabetes Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnostic Tests
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test – Measures glucose levels after at least 8 hours of fasting.
- HbA1c Test – Assesses average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) – Evaluates the body’s ability to process glucose.
- Urine Tests – Detects glucose or ketones, indicating diabetes.
Treatment Methods
- Insulin Therapy – Essential for Type 1 diabetes and some Type 2 cases.
- Oral Medications – Includes Metformin, Sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors, which enhance insulin production and efficiency.
- Dietary Management – Regulating carbohydrate intake, avoiding sugary and starchy foods.
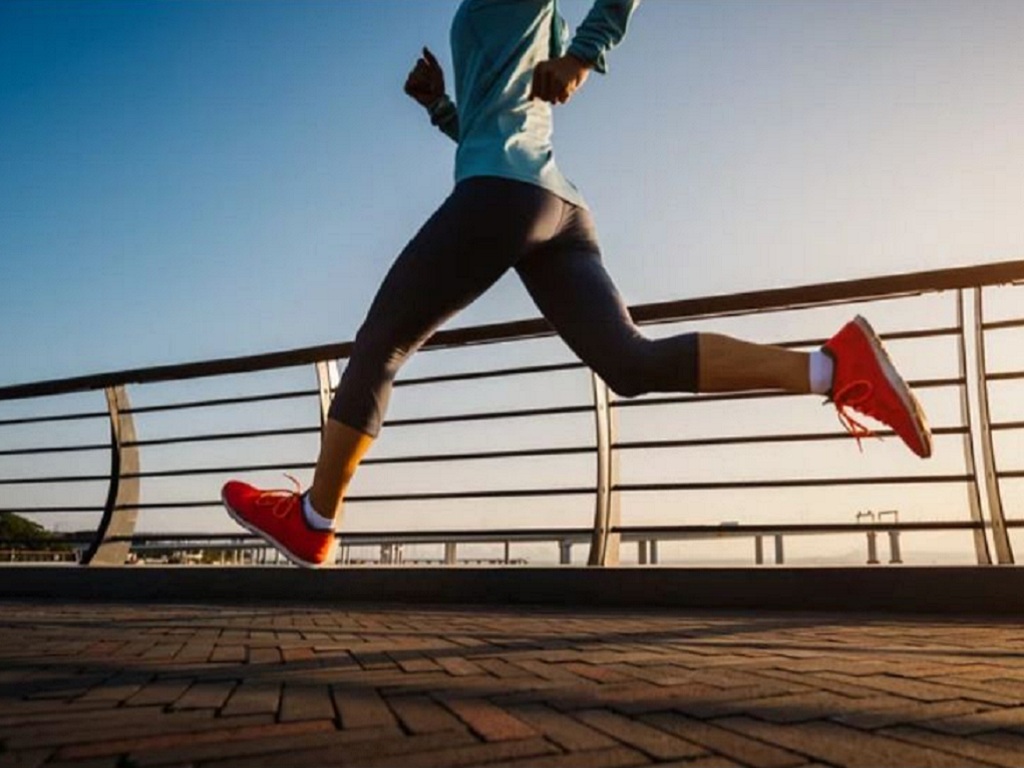
- Exercise – Improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Regular Health Monitoring – Essential for tracking treatment effectiveness and preventing complications.

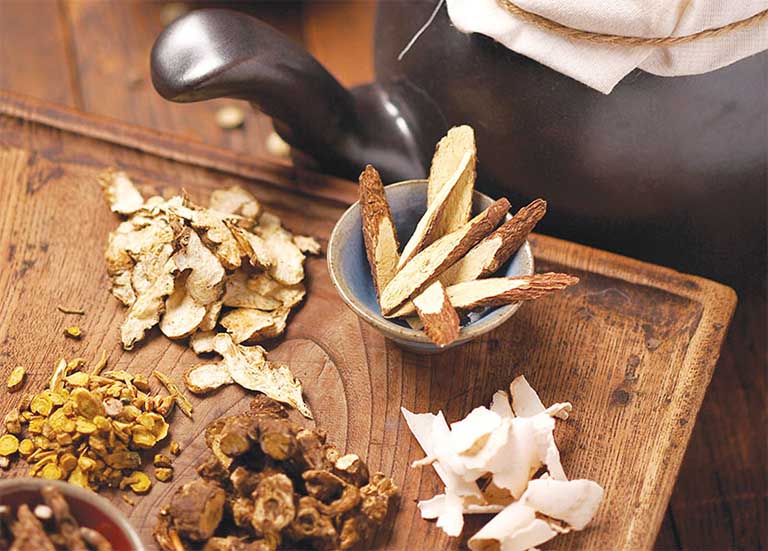
Traditional Medicine Perspective on Diabetes
In Traditional Eastern Medicine, diabetes is known as “Xiao Ke” (Wasting and Thirsting Disorder) and is categorized into three types:
- Upper Type: Excessive thirst and dry throat.
- Middle Type: Excessive hunger and rapid digestion.
- Lower Type: Frequent urination with clear urine.
Causes in Traditional Medicine
- Emotional Stress (Qi Imbalance): Prolonged stress, anxiety, and depression disrupt organ functions.
- Unbalanced Diet: Overconsumption of sweet, fatty, and spicy foods damages the Spleen, Liver, and Kidneys.
- Qi and Blood Deficiency: Weakness in Qi and Blood circulation impairs organ function, particularly the Spleen, Liver, and Kidneys.
Traditional Medicine Treatments for Diabetes
Herbal Remedies
Traditional Medicine utilizes herbal formulas to support pancreatic function, improve metabolism, and regulate blood sugar levels. Commonly used herbs include:
- Chinese Yam (Hoài Sơn) – Strengthens the Spleen and Kidneys, supports glucose metabolism.
- Rehmannia Root (Sinh Địa) – Clears heat, nourishes Yin, alleviates excessive thirst and dry mouth.
- Ophiopogon Root (Mạch Môn) – Moistens the lungs, generates fluids, relieves dryness and persistent thirst.
- Goji Berry (Kỷ Tử) – Enhances Liver and Kidney function, improves overall health and glucose control.
- Schisandra (Ngũ Vị Tử) – Regulates blood sugar and liver function.
- Alisma (Trạch Tả) – Diuretic properties, aids in reducing excessive urination.
- Poria Mushroom (Phục Linh) – Supports digestion and immune health, helps lower blood sugar levels.
- Astragalus (Hoàng Kỳ) – Boosts Qi and circulation, supports immune function and glucose regulation.
These herbs are often combined into formulas to maximize effectiveness. However, they should be used under the guidance of a Traditional Medicine practitioner to ensure safety and effectiveness.

Acupuncture Therapy
Acupuncture targets specific points such as Tai Xi (Kidney 3), San Yin Jiao (Spleen 6), and Zu San Li (Stomach 36) to enhance Qi flow, regulate circulation, and improve organ function.
Dietary and Lifestyle Recommendations
- Maintain a balanced diet – Avoid excessive sweet and greasy foods, eat fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains.
- Regular exercise – Engaging in moderate activities like walking, swimming, or cycling supports blood sugar control.
- Stress Management – Meditation, Tai Chi, and deep breathing exercises help balance Qi and improve insulin sensitivity.
Effective Diabetes Prevention Strategies
- Maintain a healthy weight – Prevent obesity and maintain an ideal BMI.
- Adopt a nutritious diet – Reduce sugar, salt, and saturated fats, while increasing fiber, whole grains, and vegetables.
- Engage in regular physical activity – At least 30 minutes of daily exercise is recommended.
- Routine health check-ups – Monitor blood sugar levels and potential risk factors for early detection.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a chronic but manageable condition when individuals are proactive in understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
By combining modern medicine with Traditional Eastern Medicine, along with a balanced lifestyle, individuals can effectively control blood sugar levels and prevent severe complications.
Try Kanpo 223 – a traditional Japanese herbal formula designed to support blood sugar control and overall metabolic health!