
Stomach Pain
Stomach Pain
Stomach Pain and the Support of Herbal Medicine
Overview of Stomach Pain
Stomach pain is one of the most common digestive disorders today, affecting millions of people worldwide. This condition not only causes discomfort but can also lead to severe complications if not treated promptly and properly. Stomach pain often manifests through symptoms such as:
- Epigastric pain: Sharp or dull pain in the upper abdomen, usually occurring after eating or when hungry.
- Nausea and vomiting: A feeling of nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting of food or gastric acid.
- Acid reflux and belching: Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation behind the breastbone.
- Indigestion: A feeling of heaviness, bloating, and discomfort after eating.
- Unexplained weight loss: Weight loss due to impaired digestion and nutrient absorption.
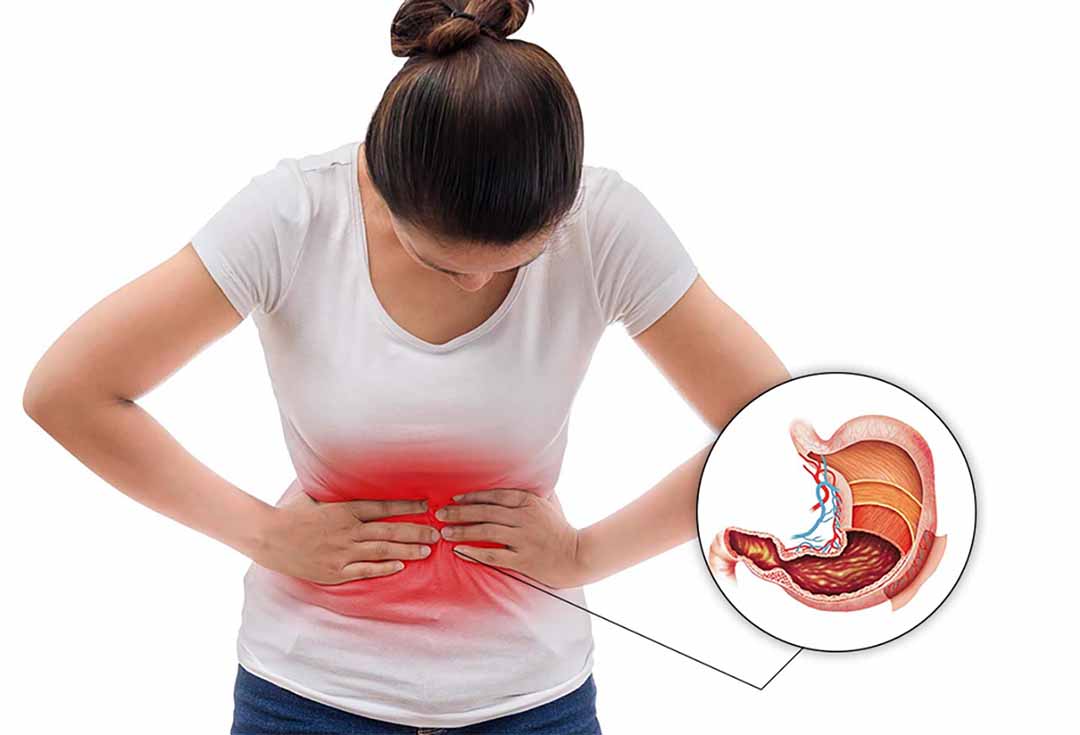
How the Stomach Works and Causes of Stomach Pain
The stomach is a vital organ in the digestive system, responsible for breaking down food and mixing it with gastric juices, facilitating nutrient absorption. When the protective mucosal lining of the stomach is damaged or weakened, stomach acid can attack the tissues, leading to inflammation and ulcers. Several factors, including H. pylori bacteria, NSAIDs, stress, and unhealthy dietary habits, can contribute to this damage, resulting in stomach pain and gastritis.
Common Causes of Stomach Pain
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Infection: One of the most common causes of stomach ulcers. H. pylori bacteria attack the stomach’s protective lining, leading to inflammation and ulcers, causing stomach pain.
- Use of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, commonly used for pain relief and inflammation, can damage the stomach lining when taken long-term or in high doses, leading to ulcers.
- Unhealthy diet: Excessive consumption of spicy, acidic, or fatty foods can stimulate excessive stomach acid production. Irregular eating habits, skipping meals, or overeating can also increase the risk of gastritis.
- Stress and anxiety: Prolonged stress can increase stomach acid production, leading to ulcers. Additionally, stress affects the gut-brain axis, reducing blood flow to the stomach and weakening the mucosal barrier.
- Alcohol and smoking: Alcohol and tobacco irritate and damage the stomach lining, reducing its ability to heal and protect itself, leading to inflammation and ulcers.
- Duodenal ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): These conditions can damage the stomach and esophageal lining, leading to inflammation, ulcers, and stomach pain.
- Genetic predisposition: Some people have a higher risk of stomach disorders due to genetic factors. If a family member has a history of gastric ulcers, the risk is increased.
- Aging: As people age, the stomach lining’s ability to protect itself weakens, and the increased use of NSAIDs or other medications raises the risk of ulcers.
Recognizing and preventing these causes is crucial in maintaining digestive health and reducing the risk of stomach pain.
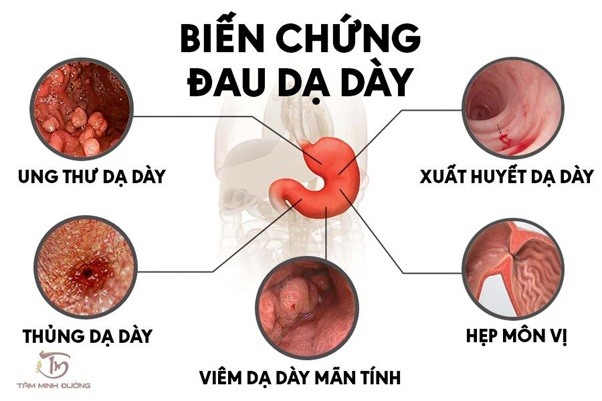
What Are the Risks of Untreated Stomach Pain?
If left untreated, stomach pain can lead to severe complications, including:
- Peptic ulcers: Damage to the stomach lining can deepen, forming ulcers that cause intense pain and even internal bleeding.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding: Ulcers can lead to internal bleeding, which manifests as vomiting blood or passing black stools, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Stomach perforation: If an ulcer penetrates through the stomach wall, it can cause a life-threatening condition known as peritonitis, requiring emergency surgery.
- Stomach cancer: Chronic gastritis, if left untreated, can lead to malignant changes, increasing the risk of stomach cancer.

The Role of Herbal Medicine in Supporting Stomach Pain Treatment
In traditional medicine, herbal remedies have been used for centuries to treat digestive disorders, including stomach pain. These herbs not only relieve symptoms but also help protect and restore the stomach lining, reduce inflammation, and prevent H. pylori infection.
Common Herbal Remedies for Stomach Pain
- Licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra): Licorice is known for its anti-inflammatory and mucosal-protective properties. Its active compound, glycyrrhizin, inhibits H. pylori growth, promotes ulcer healing, and relieves pain.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Turmeric contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory agent. Curcumin not only reduces inflammation but also stimulates mucus production to protect the stomach lining and prevent new ulcers.
- Tangerine peel (Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae): Tangerine peel aids digestion, reduces bloating and indigestion, and regulates gastrointestinal function, alleviating stomach pain caused by digestive disorders.
- Atractylodes (Atractylodes macrocephala): Atractylodes enhances digestive function, improves nutrient absorption, and protects the stomach lining from harmful factors.
Benefits and Limitations of Herbal Medicine
Using herbal medicine for stomach pain treatment offers several advantages, such as:
- Fewer side effects compared to conventional medications.
- Improved overall digestive health.
- Enhanced natural healing and protective mechanisms of the stomach.
However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before using herbal remedies, especially if taking other medications, to avoid potential drug interactions.
Conclusion
Stomach pain is a common condition that can lead to severe complications if not managed properly. Herbal medicine, with its long history in traditional medicine, can play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and supporting stomach health. However, combining herbal remedies with modern treatments and professional medical supervision ensures safe and effective outcomes.
Try Kanpo 203 to experience the benefits of traditional Japanese medicine for safe and effective stomach pain relief!