
What is Glucosamine? Why Should Middle-aged People Care?
What is Glucosamine? Why Should Middle-aged People Care?
What is Glucosamine?
Glucosamine is a natural compound formed from glucose and an amino acid. The human body produces it and stores it in cartilage, joints, and connective tissue. However, production gradually declines with age, which may lead to joint stiffness and pain.
To compensate, manufacturers extract glucosamine from fungi or animal shells, especially from crab, shrimp, and lobster, and turn it into convenient supplement forms.
Common Types of Glucosamine
Glucosamine supplements come in several forms, including:
-
Glucosamine Sulfate
-
Glucosamine Hydrochloride
-
N-Acetyl-Glucosamine
Among these, glucosamine sulfate and hydrochloride are most commonly used to support joint health. Manufacturers offer them in tablets, capsules, liquid extracts, and even topical creams for user convenience.
How Glucosamine Supports Joint Health
Joints allow bones to move freely. They contain cartilage, synovial fluid, and ligaments that cushion and stabilize movement. Over time, cartilage can wear down, causing bones to grind together. As a result, people experience joint pain, inflammation, and loss of flexibility.
Glucosamine offers several key benefits:
-
It helps the body repair and regenerate cartilage.
-
It protects cartilage from breakdown.
-
It boosts the production of synovial fluid, improving lubrication.
-
It relieves symptoms of osteoarthritis and other joint disorders.
-
It may slow down joint degeneration in aging adults.
Moreover, some research shows that glucosamine can assist in managing other conditions, such as interstitial cystitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and even glaucoma.
Dosage and How to Take Glucosamine
Most experts recommend a daily dose of 1,500 mg. This dosage supports joint function without causing side effects for most people. However, users should consult a doctor for the best results.
You can take glucosamine before or after meals. Taking it with food may reduce stomach discomfort.
Should You Take Glucosamine With Food?
Yes. Although glucosamine works regardless of timing, taking it during or after meals can reduce nausea or upset stomach. This is especially helpful for people with sensitive digestion.
Can You Take Glucosamine Every Day?
Yes. Daily glucosamine supplements benefit people with osteoarthritis or joint degeneration. Regular intake supports joint function and reduces pain over time. However, results appear gradually, so consistency is essential.
Always follow your doctor’s advice and avoid exceeding the recommended dose.
Who Should Not Take Glucosamine?
Although glucosamine is generally safe, some people should avoid it:
-
People allergic to shellfish such as shrimp, crab, or mussels.
-
Pregnant or breastfeeding women.
-
People with diabetes, asthma, or chronic infections should speak to a doctor before use.
How to Choose a Quality Glucosamine Supplement
Because many products vary in quality and source, it’s important to choose glucosamine from trusted brands. Look for clear labeling, natural ingredients, and good manufacturing practices.
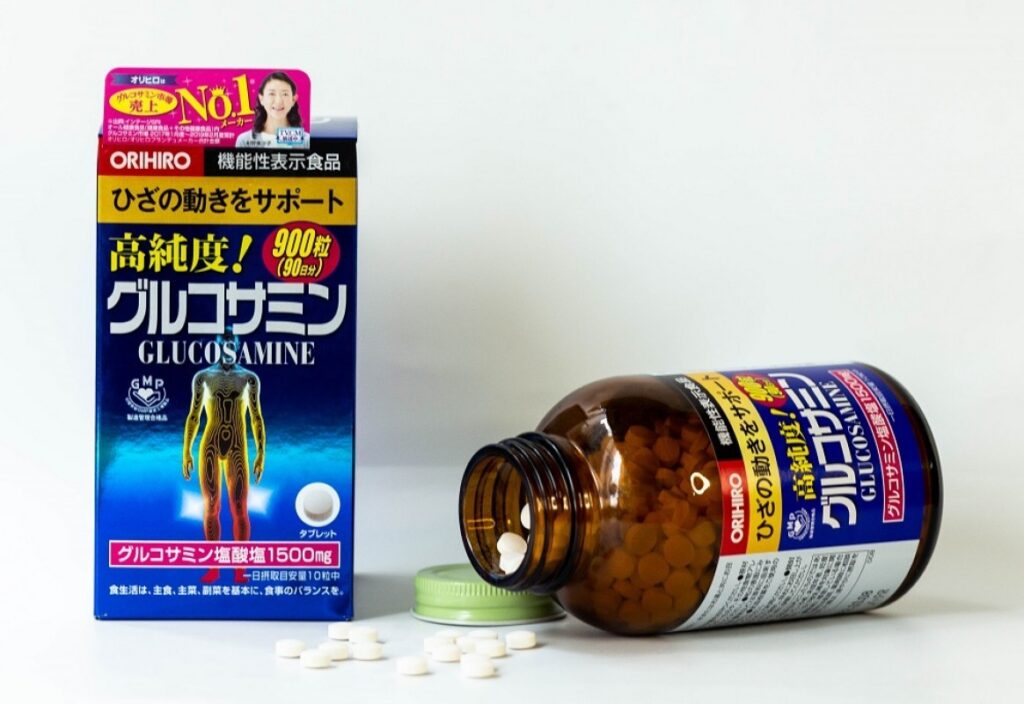
For example, the Orihiro Glucosamine 900 Tablets offer a high-quality option. This supplement uses natural ingredients to support joint health effectively, especially for middle-aged and older adults.
Conclusion
Glucosamine plays a vital role in maintaining joint flexibility and comfort. For middle-aged individuals, using the right supplement can help ease pain, slow down joint damage, and support mobility. Therefore, combining glucosamine with a balanced diet and regular exercise can greatly improve your quality of life.